Now there are many different methods and approaches to routing incoming calls, so it’s easy to get confused. So how do you know which method is best suited for the current level of development of your organization? Or perhaps you should use a combination that includes several strategies at once. Below we will give our translation of the article, which describes ten different routing methods, and help you choose the right one, depending on the level of your own contact center.
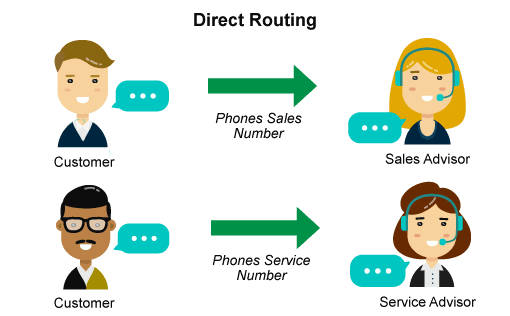
1. Group hunt (direct routing)
New or smaller organizations tend to provide a basic level of customer service. They just want to route cases to the right department within their business. In this case, direct routing is the standard option. When a customer needs to buy something, he calls the number of the sales department and waits if the line is busy. For service or other issues, a separate number is required. The call is first directed to a specific employee and, if the line is busy, goes to the next operator.
2. Least Idle or minimal operator idle
Using an Automatic Call Distributor (ACD) allows you to move from direct routing to a more sophisticated strategy that minimizes agent downtime. So the call will be distributed to the specialist who was waiting for the call longer than the others. 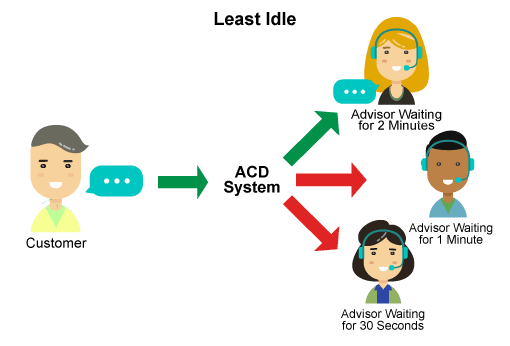
3. Distribution to the least employed
Least Occupied Routing(LOR) When allocated to the least busy operator, the call goes to the employee who received the least number of incoming calls during the day. This circumvents the “me-at-the-end-of-the-queue” game, in which consultants go into a ready state and then into a waiting state, which moves them to the back of the call queue. The term “busy rate” in the illustration is the percentage of time the counselor spends in conversation throughout the day. The overall employment rate of all employees is useful in performance calculations and helps determine how many managers should be in a call center. 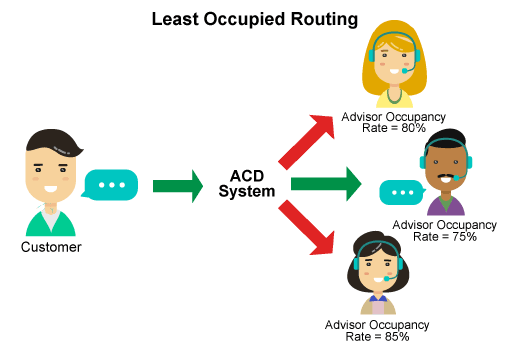
4. Routing by skill level
Skills-Based Routing Skill-based routing selections help ensure efficient customer service and reduce wait times. You can help improve the quality of customer service by providing the customer with the “most suitable” consultant with a caller. As a result, multidisciplinary operators will need to assign skills as well as a skill level for each assigned skill. An example of this is the referral of a foreign caller to a consultant who can speak his language. 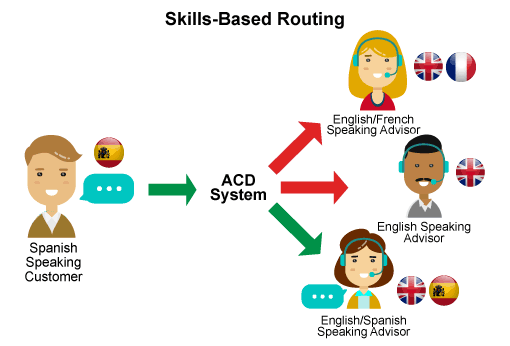
5. Dynamic Routing and Quality of Service
Choosing only on the skill level does not guarantee happy customers. First of all, this is due to the fact that he will have to wait too long for a consultation. Dynamic routing takes into account the skills of specialists, and also estimates the predicted waiting time. This allows you to provide better customer advice within a given level of service. For example, if the approximate wait time for a specialist with the desired skill is too long, “reserve” operators can be added to the queue, who will serve the client faster, albeit possibly at a less competent level. 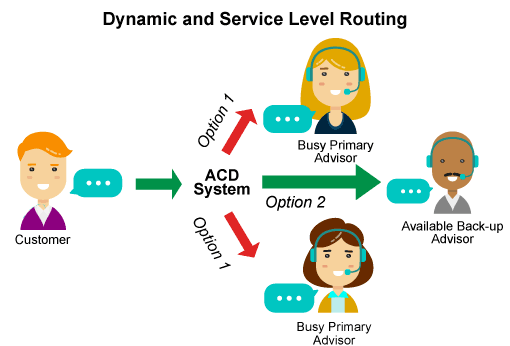
6. Routing business rules
Once your ACDs and routing mechanisms are in place, you can begin to customize your call routing strategy to support specific business goals, such as: ● Routing complex calls to specially trained agents. ● Connecting customers with low satisfaction scores to individual professionals who specialize in increasing loyalty. ● Allow callers to connect with the consultant they last spoke with. 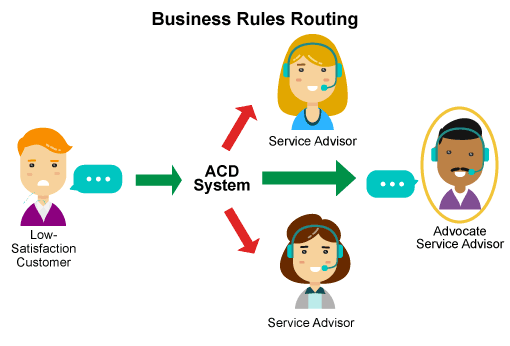
7. Data-Directed Routing
Having made their own routing strategy, call centers can choose data-based routing as the next step in call processing. It will help distribute calls based on customer data. For example, a bank customer, a credit card holder, may call with a request, but if his payment is late (this will be determined during initial identification), then the call is redirected to the collection department. Integrating the initial IVR ID process with current customer data can provide a powerful business solution. Identifying customers in the early stages of a call opens up many possibilities, such as redirecting calls to consultants or service professionals who have previously dealt with the customer. 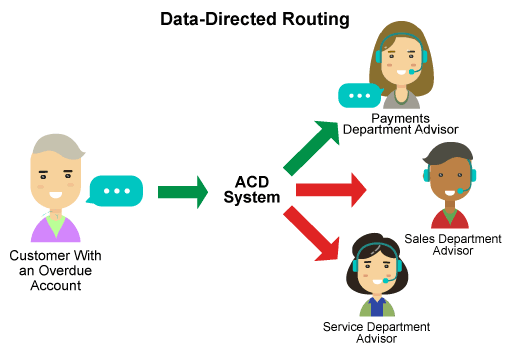
8. Cost Based Routing
This combination of customer identification with more detailed information from CRM opens up new possibilities for value-based routing. The solution is built on the value, value or revenue from the client, allowing you to go beyond cost and quality of service. For example, it could be a customer of a mobile operator who called three months before his contract was renewed to clarify its details. The value-based routing system will determine that it has a higher propensity to switch carriers at this stage and will route the call to the customer retention department to ensure that the subscriber does not change his mind and remains with his current carrier. 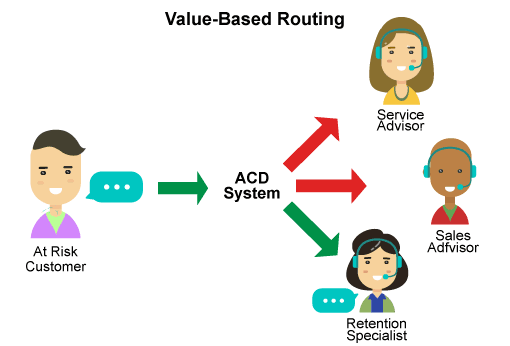
9. Outbound routing
Another important development is that routing is not always about inbound communication. While we continue to recognize the importance of traditional metrics such as average call handle time, many organizations are turning to new metrics. For example, to the consumer loyalty index, which tracks how many customers recommend their service or product. Innovative services such as outbound routing allow the mortgagee to send text messages to the client immediately after their loan application is approved. This initiative increases the likelihood that the client will recommend the company to their friends. 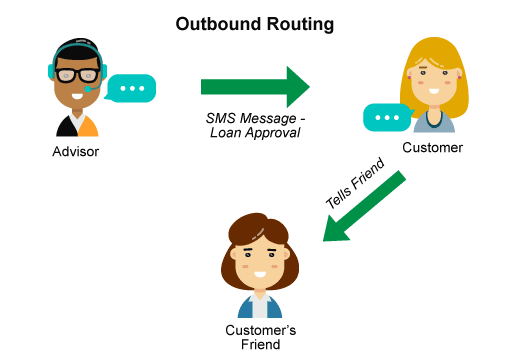
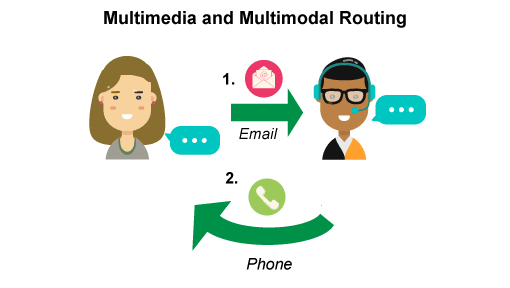
10. Multimedia and multichannel routing
Consumers interact with service providers through different information channels. They may get great voice advice, but more sales will come from a company that also allows the customer to connect in a way that is convenient for the customer. The main routing challenge faced by many call centers is not only how to support multimedia routing across multiple channels of customer contact, but also how to route these transactions in a consistent manner, be it voice, instant messengers, email, IVR or SMS. At the moment, the emphasis in the development of systems has shifted from cost effectiveness to a process that integrates customer data (history from CRM), and also allows you to make decisions in real time. This approach provides a significant increase in profits. Clearly, technology is key to this, but it’s also important that organizations get their people and processes in order to make this new generation of multimedia, multi-modal customer interactions truly work for both their customers and their own organization. Clearly, technology is a key factor in building such technology, but it is also important that organizations educate their people and streamline processes in order to make this new generation of multimedia, multi-channel customer interactions truly work for both their customers and their customers. own organization.