If you’re launching a sales department from scratch, regardless of the industry, let us say right away: there won’t be simple solutions. However, building a functional, profit-generating department is achievable. Especially if there’s a clear plan, convenient tools, and an understanding of how not to turn the process into an endless experiment. In this guide, we’ve compiled practical advice on how to organize your sales department operations and which Oki-Toki platform functions will help streamline the process.
What is a sales department and why is it needed?
How to create a sales department from scratch?
Step 1. Assessing the resources of the sales department
Step 2. How to form a sales team: roles and responsibilities
Step 3. Financial aspect and employee motivation
Step 4. Training and coaching your sales team
Step 5. Metrics for measuring productivity
How to launch a sales department with Oki-Toki
What is a sales department and why is it needed?
A sales department is a structured team whose main task is to attract, convince, and support clients throughout the entire deal process. It’s not just a “call group” or “managers for everything.” It’s a separate, important element of the company, responsible for consistent income. The format and composition of the department depend on the business:
- In outsourcing call centers, it can include: cold line agents, a dialer call processing team, incoming line employees, follow-up group, and account managers;
- For SaaS companies – sales managers, Customer success, sometimes technical consultants;
- Banking sector – bank product sales manager, financial consultant;
- Medical field – pharmacist, medical services sales manager, medical representative.
The structure of the sales department may vary, but the goal is the same – attracting clients. For everything not to fall apart- the right goal setting, clear tasks, and convenient tools are necessary; otherwise, inquiries will be lost, managers will get tired, and customers – leave.
How to build a sales team from scratch?
Building a sales team – means developing a system that consistently brings in new clients and money. The main thing is not just to hire people, but to organize a clear process: who does what and why. We suggest five steps to creating a sales department that can help avoid typical mistakes right from the start.
Step 1. Assessing the resources of the sales department
If the sales department in a call center is the engine, then starting without assessing the resources is like driving on an empty tank. Sooner or later, everything will stop. Therefore, before hiring people, writing scripts, and setting up CRM, it’s necessary to figure out what we have, what’s missing, and who will be managing it all.
Who will be responsible for the launch?
Launching a sales department doesn’t mean giving an agent a list of numbers and saying: “Sell.” It’s a project, and a specific person should be responsible for it:
- Head may take responsibility at the start, then delegate duties. It’s okay, but it’s important to honestly assess how much time he’s willing to spend on training employees, checking, and making improvements;
- Sales department head – a great option. The main thing is to empower him with real authority and not “interfere from above”;
- External consultant – sometimes, it’s simpler to involve a contractor who will help with the organization of processes, and then the manager will take everything under control.
Important! Project launch should be managed by one person – it helps avoid confusion in tasks, double decisions, and situations where “no one is responsible for anything.” One responsible person means single control, clear deadlines, and quick decisions if something goes wrong.
Defining goals and setting tasks
These aren’t just abstract words. Goals should be clear and measurable so that later it’s apparent whether they were achieved or not. And tasks are steps that help these goals come to fruition. It’s important that they are specific and time-bound: “make 50 calls a day” or “hold 10 meetings a week.” Everything should be understood and achievable – so the team knows what to do and what to strive for.
What is needed for the start?
When the goals of the sales department are set, it’s time to think about the material and technical base. For starters, answer the following questions:
What will be the format of the department? Will operators be located in the office or work from home? If the budget is tight, you can hire remote employees and monitor them by reports. For office work, additional resources will be needed – the office itself, computers, stable internet, headsets, etc. The technical base, in this case, must be prepared in advance.
What means of communication will be used? Mobile devices, PBX, softphones – choose the appropriate option.
Are additional communication channels needed? Chats, messengers, website, SMS, and emails can increase conversion.
Is there a database of numbers? A quite logical question, also needs to be taken care of in advance. Outsourcing sales departments receive databases from clients. The second option – collect the database independently, it is a lengthy process, but as a result – only the contacts of target customers.
Will there be scripts? Will your agents improvise or voice the text according to a ready-made template? If you choose the second option – it will provide structure, a step-by-step dialogue, and agents will not “get lost” during the conversation.
Who will accompany the client after the sale? At the start, it can be an agent or someone from the team who knows the product. But it is important to define steps: who sends the contract, who is responsible for the launch, who contacts after a week. It’s best to describe these actions in the form of a list or diagram.
How to keep reporting? You can use Excel or special programs. For large departments, a cloud system or CRM is better, where everything is updated automatically and easily tracked in real-time.
Who will train employees and monitor work This role can be taken by the manager himself, sales department head, or supervisor. The main thing is not to leave new employees without feedback.Answers to these simple questions will help you determine priority tasks, for example, purchasing new software. When choosing software, be guided by the “all-in-one” principle. The more requests the service covers, the simpler the organization of the work process.
How many employees can you involve at the start?
You can start even with a couple of agents, and then gradually expand. When hiring for sales departments, several factors need to be taken into account:
- Volume of calls – logically, the more calls, the more agents needed. It’s necessary to consider both the number of outgoing calls and incoming calls, and the work of the dialer.
- Conversion to sales – it’s the percentage of leads (clients) who become real buyers. Calculated as the ratio of the number of closed deals to the total number of leads. At the creation stage, this will be an estimated value.
- Goals of the department – it’s the plan that needs to be achieved. Here it’s necessary to consider how much an average employee can sell, demand fluctuations, lead quality, and other factors that affect work efficiency.
- Complexity – consider the product’s features, as they can significantly affect the time needed for a deal. If the product requires a lot of explanations or has technical specifics, the deal may take more time. For simple products, the process will be faster.
- Working hours – here it’s important not how many working hours an agent has, but the average deal time – the time from the first contact to purchase. For some products, it’s an hour, for others – a week. This depends on many factors: database quality, product complexity, and sales manager skills.
The number of employees will depend on these factors. Starting with a small team, you can gradually increase it as the working processes and demand grow.
Step 2. How to form a sales team: roles and responsibilities
You can’t just sit 5 people down and say, “Call.” Everyone should have their area of responsibility. Especially if you want a managed process, not chaos. Basic roles in the sales department might be:
- Cold-calling agent – calls the database, works according to scripts, generates initial interest;
- Sales manager– formally the same agent who picks up the client and completes the payment;
- Account manager – manages the client after purchase: helps to understand the product, answers questions, offers additional services, and does everything to keep the client for a long time and, if desired, buy more;
- Supervisor/Manager– watches over results, motivation, quality of dialogues.
The sales team structure should be adjusted based on company business processes. Some roles may not exist, for example: one employee can perform the role of a sales manager and will be assigned to a “successful” client after the deal. In the distribution of duties, it’s important that everyone knows their responsibilities and does not go beyond their authority.
Step 3. Financial aspect and employee motivation
To motivate employees to work, outline what bonuses they can receive and for what. The salary rate is the minimum threshold, but it doesn’t always motivate an agent to take action and career growth. Develop a bonus system, where it’s specified how much needs to be done to get a bonus. It can be a percentage for sales, individual fixed bonuses for ideas, team assistance, retaining customers. Incentives motivate, but sometimes a “stick” has to be present too. Determine situations for which there can be fines, for example: being late for a shift, absence without leave, etc.
Step 4. Training and coaching your sales team
At the initial stage, it’s necessary to tell employees about the product and how to sell it. You can prepare an introductory course for “newbies”:
- Simple product description and its benefits for the customer (information materials, presentations, video tutorials);
- Short guide on using the service for call processing;
- Basic call script or chat dialogue, a list of common objections and answers to them;
- Procedure after the operation (handover, documents, settings, etc.).
And that’s quite enough for the start. But for employees not just to learn the script, but to use it properly, it’s crucial to build a sales and support training program. Periodically it’s necessary to return to analyzing calls: review them together with the employee, identify what went well and what didn’t. It can be both a regular training and a one-time consultation focusing on problematic aspects of work. The main thing is not just to point out the agent’s mistakes but to analyze how to do it best.
Step 5. Metrics for measuring productivity
If you don’t measure effectiveness, you lose it. Therefore, a sales department cannot be built without metrics. The main ones:
- Number of touches – how many times a manager tried to contact the client: calls, letters, chats;
- Conversion by stages – number of calls that turned from talks into meetings and deals;
- Average deal time – how long does the process from the first contact to payment last;
- Repeat inquiries – percentage of clients who returned after the first purchase;
- Quality of communication – agent’s ability to interact with the client, solving their issues and creating a positive impression.
By tracking metrics, you can quickly identify weak spots in the sales process and improve them. Each metric helps precisely adjust the department’s work, enhance its productivity, and improve interaction with clients. The main thing is not to overload employees with numbers, but to track what really affects the result. Metrics aren’t a reason for reproach, but a tool to improve the process together.
How to launch a sales department with Oki-Toki
Oki-Toki is a multifunctional system suitable for the sales department. To start working in the service, just choose the appropriate communication provider. Everything else is already inside the platform.
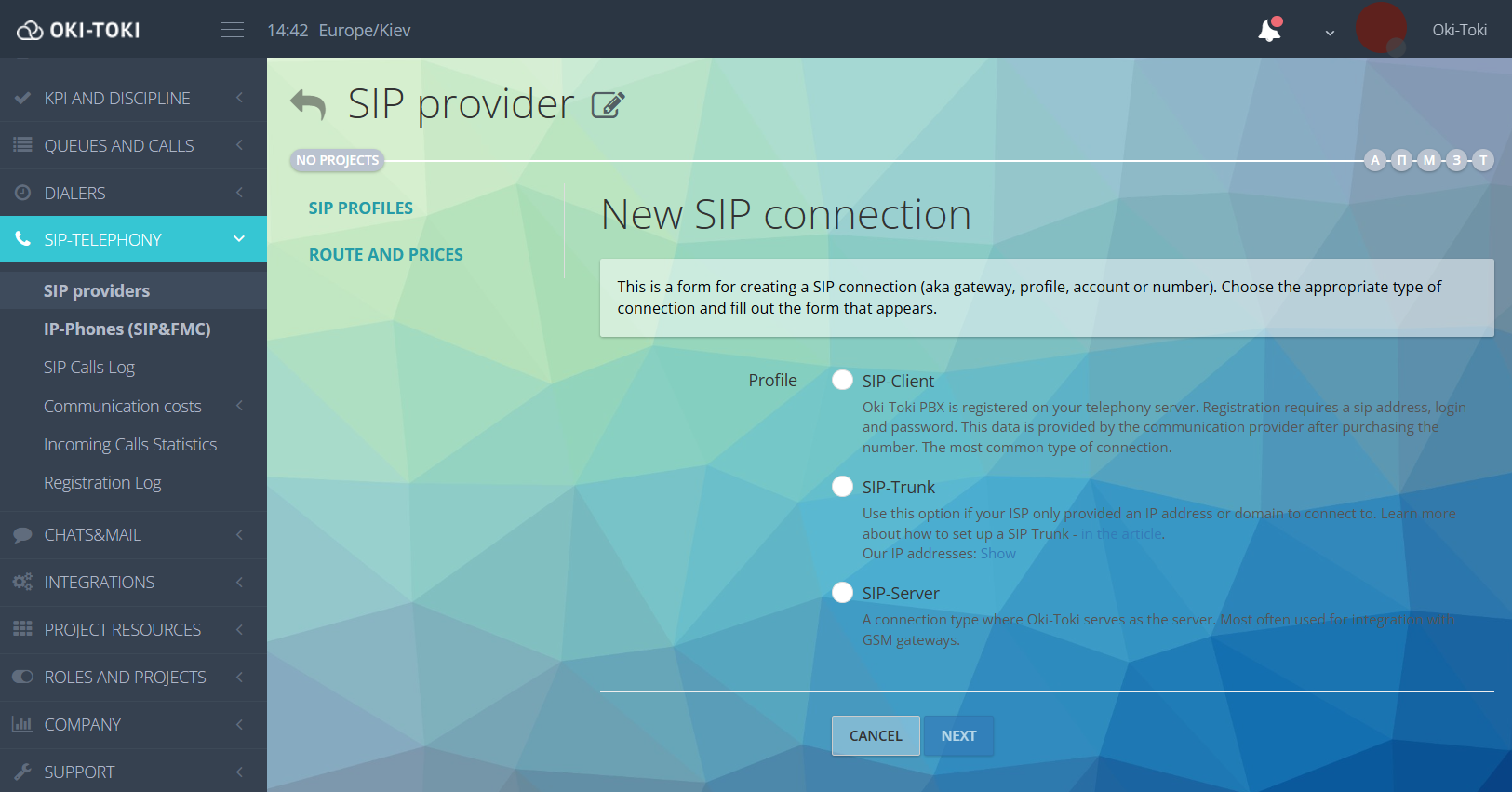
- Telephony and communication tools – in Oki-Toki, there are various connection options – you can choose the one that suits: SIP-client, Trunk, SIP-server or softphone. Everything is flexible and will be configured to your conditions.
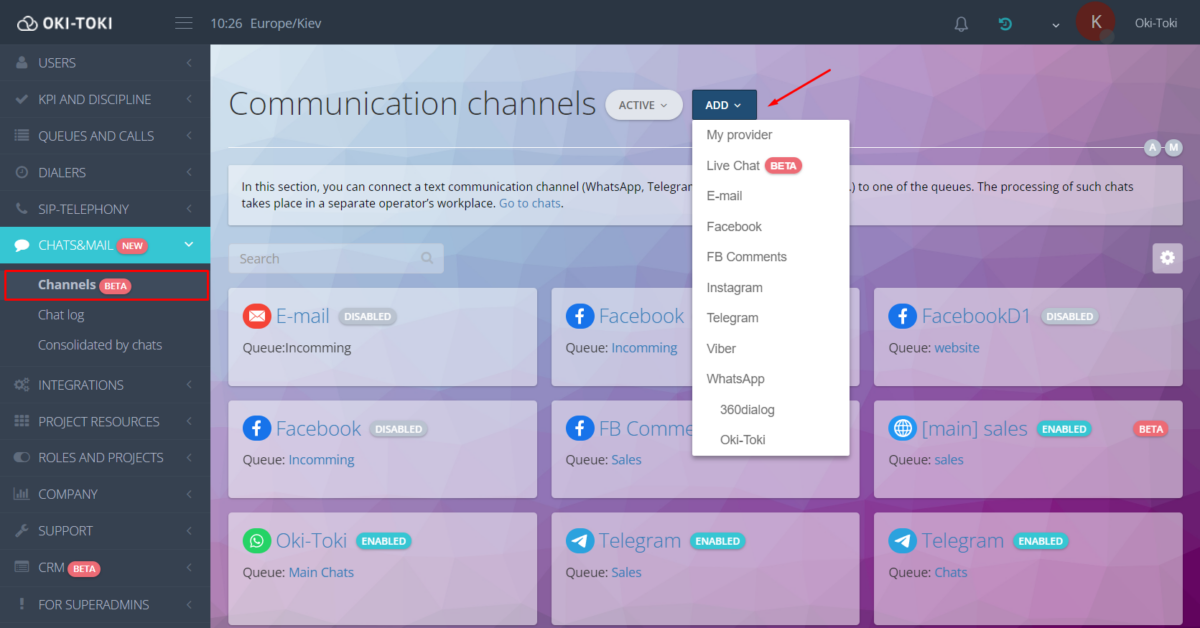
- Communication channels – in Oki-Toki, communicating with clients can be done not only by calls but also through messengers, social networks, SMS, or e-mail. The main advantage – all communication channels are gathered in one omnichannel platform.
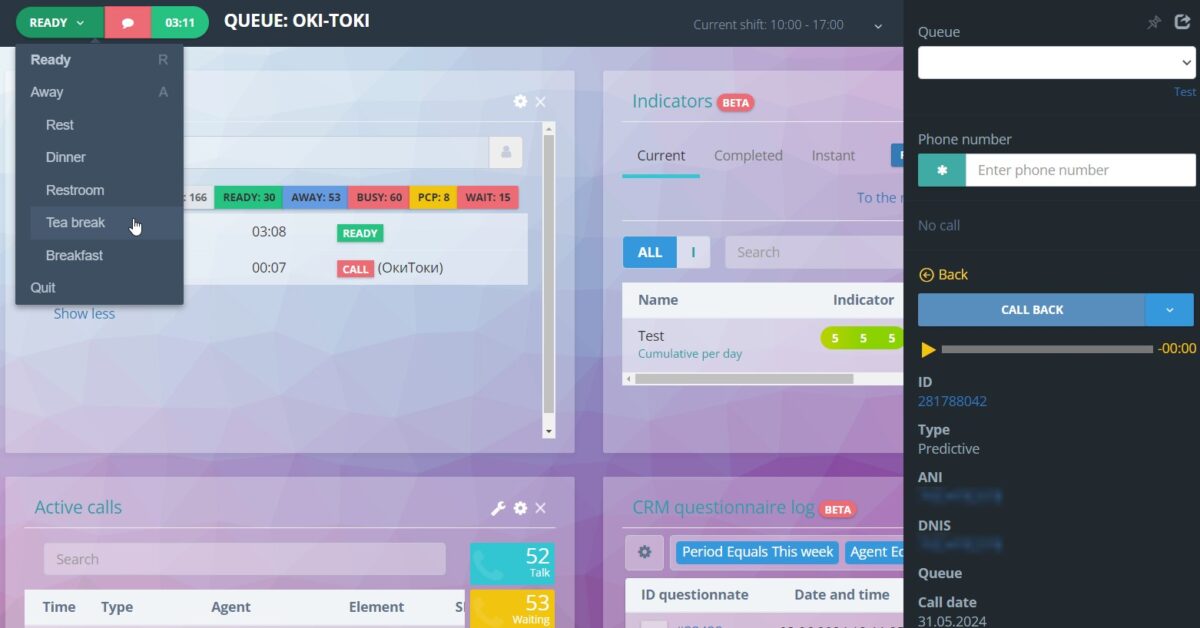
- Agent workspace – the main tool for work. All calls, forms, widgets, and information about clients are available just a few clicks away.
- System of roles and projects– in Oki-Toki, you can configure what’s visible and accessible to whom. Each employee has their own role and access level. For each independent business process – its own project. This easily separates the sales department from technical support, and a contractor from an internal team.
- Dialers – a tool for automatic dialing of a number database or mass sending of voice messages. You can select the appropriate mode, schedule, smart dialing rules, priorities, and at the end get statistics. Dialers save time, reduce the workload on the team of agents, and help “softly” inform clients or conduct full-fledged coldsales.
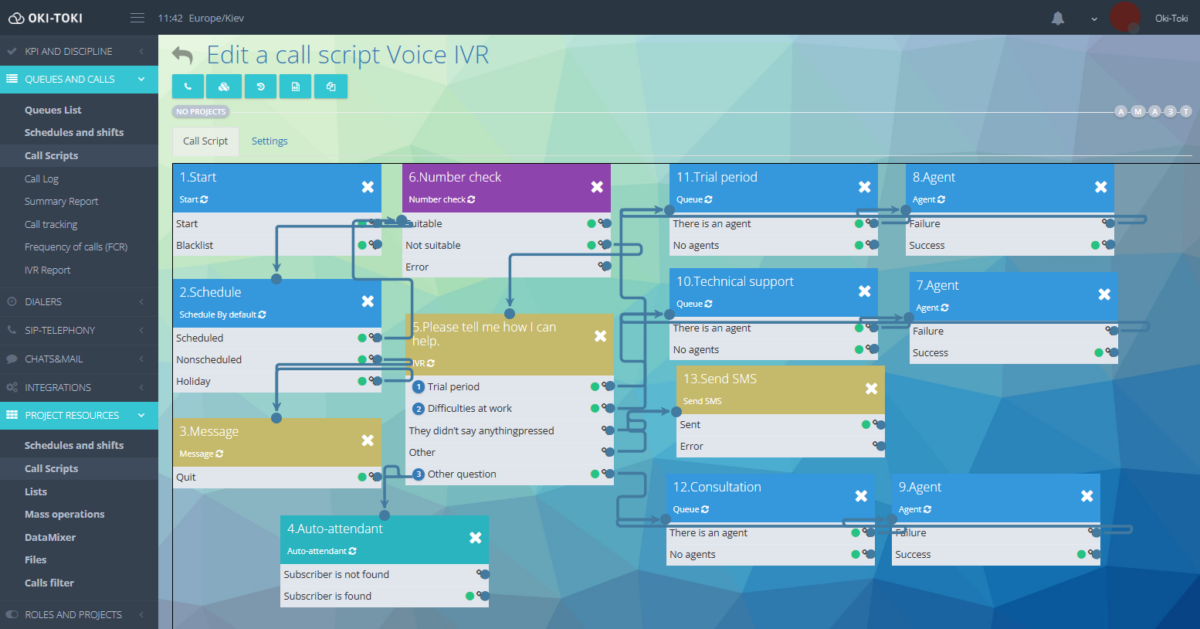
- Oki-Toki CRM – stores the history of communication with each client. Agent script can be adapted to the necessary business logic. And contact fields are useful for organizing and storing information about clients. Scripts ensure agents stay on track during conversations because they can outline text for agents, prompts, and various response options to client questions.
- API and integrations – with open API, you can transfer data, create tasks, launch scripts. Integrations with popular services already exist, the rest can be configured as needed.
- KPI and discipline – a way to keep everything under control. The system automatically calculates KPI indicators – time on the line, in conversation, on break. Breaches of norms, lateness, and absences can be reviewed in the KPI Journal.
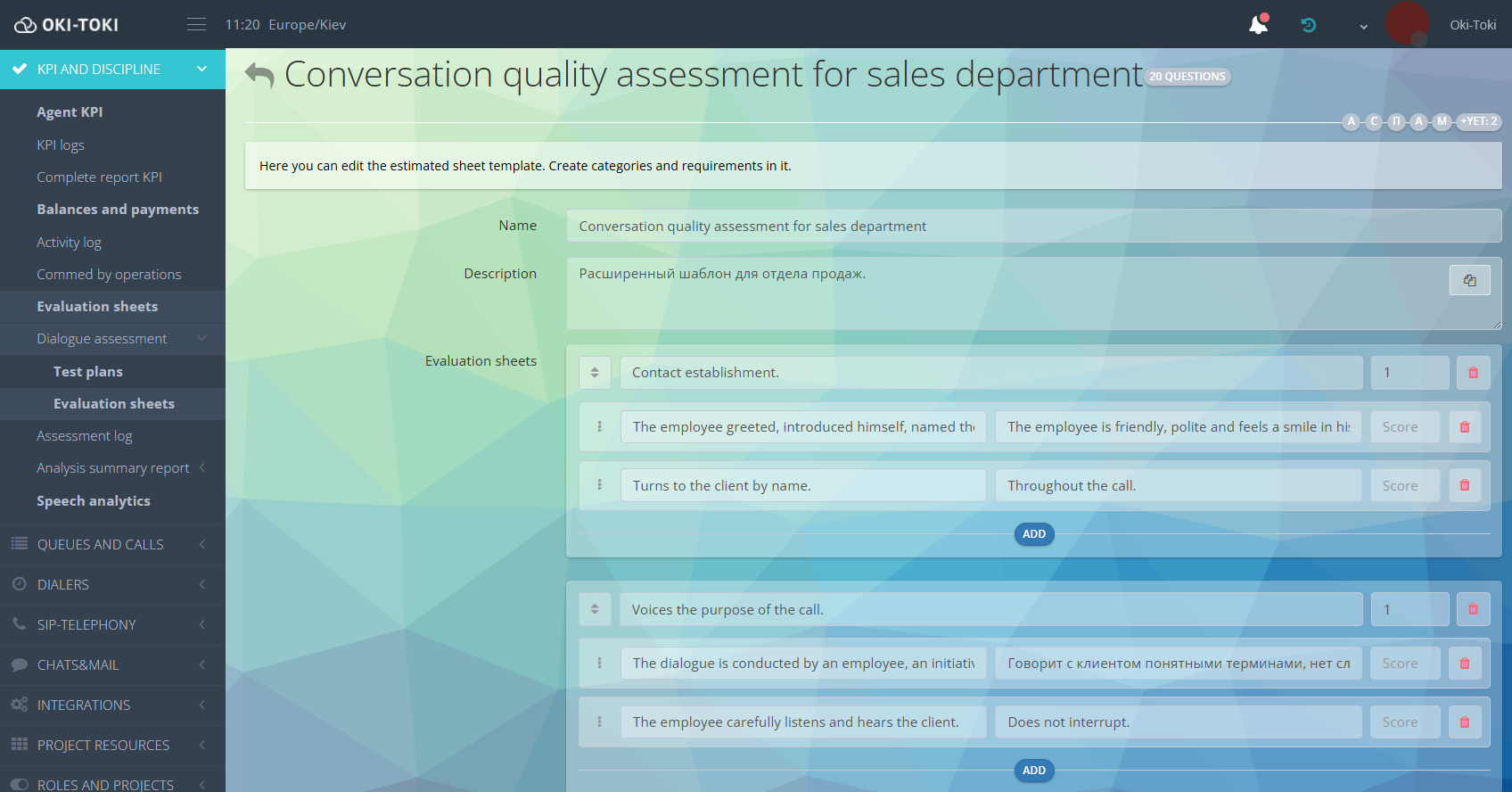
- Agent evaluation – quality control of customer service can be simplified with Evaluation Sheets. QM team will conduct checks according to the plan and template. The option to change the agent’s voice minimizes cases of “biased” treatment of employees.
- Reporting – an important part of not only the sales department’s work but the call center as a whole. In Oki-Toki, there are more than 36 reports. Data can be filtered by period, project, employees, transferred via API, and exported in a convenient format (HTML, Excel, and Google Sheet). It’s not just tables – it’s a real picture of the team’s work, all clear and simple.
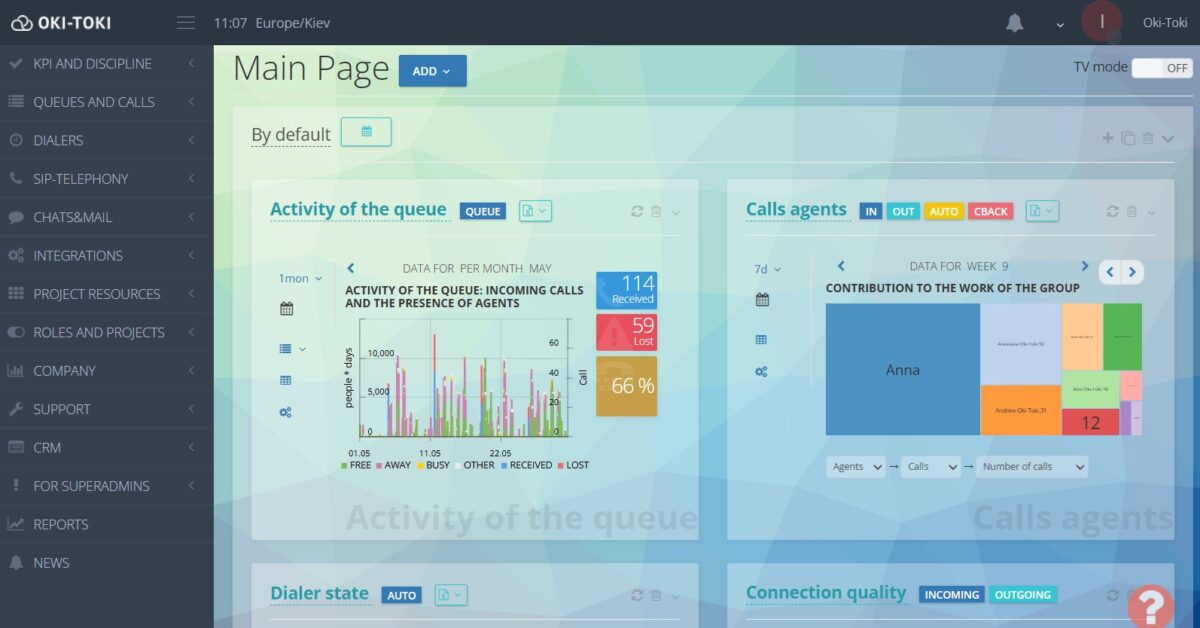
- Real-time monitoring – with Oki-Toki widgets, you can view the department’s work “in the moment”: who’s on the line, on break, or busy in conversation.
- Training tools – transcripts, call recordings, listening mode or prompter can be used for call dissections or during training sessions.
Launching a sales department is not an easy task, but with the right approach, it becomes entirely feasible. We hope our recommendations and instructions will help you efficiently organize the process, and Oki-Toki will provide automation for all key tasks. Leave a request, and we will help you with this!



